Oil & Gas Industry

The Oil and Gas (or Petroleum) industry benefits our daily lives in many ways.
Its products underpin modern society, supplying energy to power industry and heat homes, fuel for transport to carry goods and people all over the world, and providing the raw materials used to produce many of the everyday items we take for granted.
ecom helps this industry to improve in many areas including safety, operational efficiency and collaboration, spanning the complete asset lifecycle from Construction to Operations & Maintenance and finally to Decommissioning.
Petroleum
Petroleum is a general term for Oil and Natural Gas.
Oil and Gas are important fossil fuels formed over millions of years from the decomposition and pressurisation of algae, plankton and other organisms deep underground. This process forms hydrocarbons, which are compounds consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon that are powerful combustible fuels.
Petroleum is vital to many industries, and is of importance to the maintenance of industrial civilisation in its current configuration, and thus is an important industry in itself for many nations.
Oil
Oil is the world’s most important fuel and underpins our high standard of living. It provides modern convenience and freedom of movement and is crucial to transport systems.
Oil refining produces transport fuels, such as petrol (gasoline), diesel and jet fuel, as well as heating oils such as kerosene.
By-products from oil refining are also valuable. They are used in the production of plastics and chemicals, as well as many lubricants, waxes, tars, asphalts and even pharmaceuticals. Nearly all pesticides, solvents and many fertilisers are made from oil or oil by-products.
Natural Gas
Gas is a reliable, cleaner-burning fuel which offers the best combination of abundance, cleanness, affordability, reliability and flexibility.
Natural Gas consists largely of methane and a mix of other hydrocarbons, and is found in several different types of rocks, including sandstone, coal seams and shale.
Gas is used to generate electricity and to power appliances such as heaters and stoves. It is also important in many industrial processes, including making fertiliser, glass, steel, plastics, paint, fabrics and many more.
Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) is natural gas which has been converted to liquid form for ease of storage and transport.
USE CASE: Shell Aviation Refueling with SAP Cloud Platform & the Tab-Ex® 01
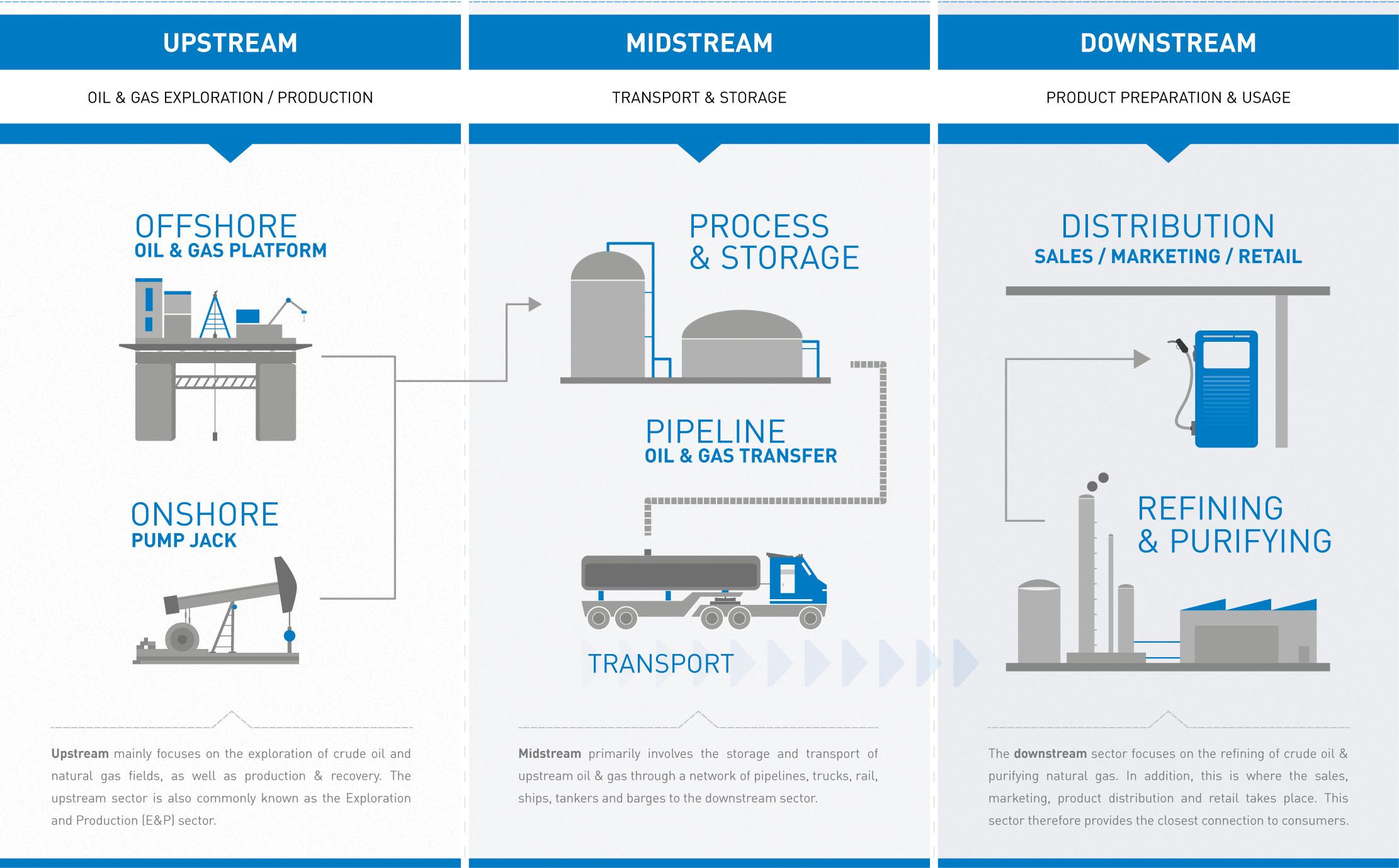
The industry is commonly partitioned into three major sectors - Upstream, Midstream and Downstream.
The Upstream sector finds and produces the petroleum – often referred to as Exploration and Production (E&P).
Exploration - petroleum reservoirs located underground or underwater are discovered by analysing the results of geological surveys and seismic surveys.
Production - once found, the Oil & Natural Gas is extracted (or “lifted”) from the reservoir primarily using drilled wells, processed, and then transported.
In its simplest form, the Midstream sector handles the processing, transport and storage of the oil and gas, including LNG. This sector provides the important link between the Upstream and Downstream sectors – gathering the extracted resources from the Upstream sector then storing and transporting it (using pipeline networks, trucks, barges, shipping tankers & rail cars) to the Downstream refining facilities, where a variety of products are produced.
Therefore Midstream is a vital sector in the Oil & Gas industry, managing one of the most difficult logistical challenges in the industrial world.
Downstream is the final step of the Oil & Gas industry process, focused on the refining of crude oil and the processing/purifying of natural gas (& LNG), and the marketing and distribution of products derived from Oil & Gas.
Examples of refined products include Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG), Gasoline/Petrol, Diesel Oil, Jet Fuel, Kerosene, Plastics, Lubricants, Asphalt and more.